Physics
Content Highlights
MCQs
Practice Quiz
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM
Practice Quiz
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTS
Practice Quiz
MCQs on Physics & Measurement
- A pressure of 106 dyne cm-2 is equivalent to
(a) 105 Nm-2 (b) 104 Nm-2
(c) 106 Nm-2 (d) 107 Nm-2
- Energy per unit volume represents
(a) Pressure (b) force
(c) Thrust (d) work
- The fundamental unit, which has the same power in the dimensional formulate of surface tension and viscosity is
(a) Length (b) Mass
(c) Time (d) None of these
- What is the power of a 100 W bulb in CGS units?
(a) 106 ergs-1 (b) 107 ergs-1
(c) 109 ergs-1 (d) 1011 ergs-1
- In the relation y = r sin(wt – kx) , the dimensional formula of w/ k are
(a) [ M0L0T0] (b) [M0L1T-1]
(c) [M0L0T1] (d) [M0L1T0]
- If the units of M and L are increased three times, then the unit of energy will be increased by
(a) 3 times (b) 6 times (c) 27 times (d) 81 times
- A suitable unit for gravitational constant is
(a) kg-m s-1 (b) Nm-1 s
(c) Nm2 kg-2 (d) kg ms-1
- One yard in SI unit is equal
(a) 1.9144 m (b) 0.9144 m
(c) 0.09144 km (d) 1.0936 km
- One light year is defined as the distance travelled by light in one year. The speed of light 3 x 108 ms-1. The same as meter is
(a) 3 x 1012m
(b) 9.461 x 1015m
(c) 3 x 1015m
(d) 4 x 1014 m
- The equation of alternating current is I=I0 e−t /CR, where t is time, C is capacitance and R is resistance of coil, then the dimensions of CR is
(a) [MLT-1] (b) [M0LT]
(c) [M0L0T] (d) None of these
- The dimensional formula of magnetic permeability is
(a) [ M0L-1T] (b) [M0L2T1]
(c) [M0L2T-1A2] (d) [MLT-2A-2]
- [ML-2T-2] Represents dimensional formula of which of the following physical quantities?
(a) Energy (b) Pressure
(c) Torque (d) Pressure gradient
13.A light-year is a unit of:
(a) Time (b) Mass (c) Distance (d) Energy
- If the dimensions of a physical quantity are given by MaLbTc then the physical quantity will be
(a) pressure if a=1, b=-1, c=-2
(b) velocity if a=1, b=0, c=-1
(c) acceleration if a=1, b=1,c=-2
(d) force if a=0, b=-1, c=-2
- In S = a + bt + ct2 , S is measured in metres and t in seconds. The unit of c will be
(a) m (b) m2 (c) ms-1 (d) ms-2
- Which of the following relations is dimensionally wrong? [The symbols have their usual meanings.]
(a) v = u- 2at (b) S = ut + 1/6 at2
(c) v2 = u2+ 2as2 / π (d) All of these
- If y=asin(bt-cx), where y and x represent length & t represents time, then which of the following has the same dimensions as that of ?
(a) (speed)2 (b) Momentum (c) Angle (d)Acceleration
18.In the equation (P+a/V2)(V-b) = constant. The units of a will be (where P is pressure and V is volume)
(a) Dyne × cm5 (b) Dyne × cm4
(c) Dyne/cm3 (d) Dyne/cm2
- Temperature can be expressed as a derived quantity in terms of any of the following:
(a) Length and mass (b) Mass and time
(c) Length, mass and time (d) None of the above
- If u1 and u2 are the units selected in two systems of measurement and n1 and n2 are their numerical values, then
(a) n1u1 = n2u2 (b) n1u1 + n2u2 = 0
(c) n1n2 = u1u2 (c) (n1 + u1) = (n2 + u2)
1. a 2. a 3. b 4. c 5. b 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. b 10. c11. d 12. d 13. c 14. a 15. d 16. c 17. a 18. b 19. d 20. a
MCQs on Kinematics
1. Any vector in an arbitrary direction can be replaced by two or three vectors
A. perpendicular to each other and have the original vector as their resultant
B. Parallel to each other and have the original vector as their resultant
C. Arbitrary vectors which have original vectors as their resultant
D. It is impossible to resolve a vector
2. If i−aj+5k→and 3i−6j+bk→ are parallel vectors then b is….
(a) 5 (b) 10 (c) 25 (d) 15
3. When a ball is thrown obliquely from the ground level, then the x-component of the velocity
(a) decreases with time (b) increases with time
(c) remains constant (d) zero
4. If the initial velocity of a projectile be doubled, keeping the angle of projection same, the maximum height reached by it will
(a) Be quadrupled (b) Be doubled
(c) Be Same (d) Be halved
5. The range of a projectile for a given initial velocity is maximum when the angle of projection is 450 . The range will be minimum, if the angle of projection is
(a) 900 (b) 1800
(c) 600 (d) 750
6. A cricketer hits a ball with a velocity 25 m / s at o 60 above the horizontal. How far above the ground it passes over a fielder 50 m from the bat (assume the ball is struck very close to the ground)
(a) 9.0 m (b) 8.2 m
(c) 11.6 m (d) 12.7 m
7. If time of flight of a projectile is 10 seconds. Range is 500 meters. The maximum height attained by it will be
(a) 125 m (b) 50 m
(c) 100 m (d) 150 m
8. Four bodies P, Q, R and S are projected with equal velocities having angles of projection 15o, 30o, 45o and 60o with the horizontal respectively. The body having shortest range is
(a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S
9. In a projectile motion, velocity at maximum height is
(a) u cosɵ/2 (b) u cosɵ
(c) u sinɵ /2 (d) None of these
10 The horizontal range of a projectile is 4√3 times its maximum height. Its angle of projection will be
(a) 900 (b) 450
(c) 600 (d) 300
11. An object is projected at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. The horizontal range and the maximum height reached will be in the ratio.
(a) 1 : 2 (b) 2 : 1
(c) 4 : 1 (d) 1 : 4
12. The maximum horizontal range of a projectile is 400 m. The maximum value of height attained by it will be
(a) 100 m (b) 200 m
(c) 400 m (d) 800 m
13. Which of the following sets of factors will affect the horizontal distance covered by an athlete in a long–jump event
(a) Speed before he jumps and his weight
(b) The direction in which he leaps and the initial speed
(c) The force with which he pushes the ground and his speed
(d) None of these
14. A ball is thrown upwards at an angle of 60o to the horizontal. It falls on the ground at a distance of 90 m. If the ball is thrown with the same initial velocity at an angle 30o, it will fall on the ground at a distance of
(a) 30 m (b) 60 m
(c) 90 m (d) 120 m
15. A football player throws a ball with a velocity of 50 metre/sec at an angle 30 degrees from the horizontal. The ball remains in the air for ( g = 10 m/s2)
(a) 2.5 sec (b) 1.25 sec
(c) 5 sec (d) 0.625 sec
16. The greatest height to which a man can throw a stone is h. The greatest distance to which he can throw it, will be
(a) h / 2 (b) h
(c) 2h (d) 3h
17. A projectile thrown with a speed v at an angle ɵ has a range R on the surface of earth. For same v and ɵ , its range on the surface of moon will be
(a) R / 6 (b) 6R
(c) R / 36 (d) 36R
18. A ball thrown by a boy is caught by another after 2 sec. some distance away in the same level. If the angle of projection is 30o, the velocity of projection is
(a) 19.6 m/s
(b) 9.8 m/s
(c) 14.7 m/s
(d) None of these
1. C 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. A 6.B 7. A 8.D 9.B 10.D 11.C 12. B 13. B 14. C 15.C 16.C 17.B 18.A
MCQs on Laws of motion
1. Three equal weights A, B and C of mass 2 kg each are hanging on a string passing over a fixed frictionless pulley as shown in the figure The tension in the string connecting weights B and C is 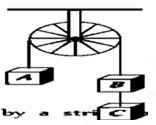
(a) Zero (b) 13 N
(c) 3.3 N (d) 19.6 N
2. Three blocks A, B and C weighing 1, 8 and 27 kg respectively are connected as shown in the figure with an inextensible string and are moving on a smooth surface. T3 is equal to 36 N. Then T2 is
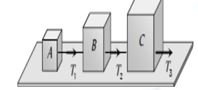 (a) 9 N (b) 18 N
(a) 9 N (b) 18 N
(c) 3.375 N (d) 1.25 N
3. Two masses m1 and m2 are attached to a string which passes over a frictionless smooth pulley. When m1 = 6 kg , m2= 2 kg the acceleration of masses is

(a) 4 m/s2 (b) 6 m/s2
(c) 5 m/s2 (d) 3 m/s2
4. The co-efficient of friction between two surfaces is μ = 0.8 . The tension in the string as shown in the figure
 (a) 18 N (b) 9 N
(a) 18 N (b) 9 N
(c) 3.375 N (d) 0 N
- A car moves at 54 km/hr to go round in a curve of radius 300m. If the road is not banked at the curve, what coefficient of friction would be required between tyres and the road?
(a) 0.075 (b) 0.025 (c) 0.01 (d) 0.02
6. If μs, μkand μrare coefficient of static friction, sliding friction and rolling friction , then
(a) μs < μk <μr (b) μk < μr < μs
(c) μr < μk < μs (d) μr = μk = μs
7. A 5 m long uniformly thick string rests on a horizontal frictionless surface. It is pulled by a horizontal force of 5 N from one end. The tension in the string at 1m from the end where the force is applied is:
(a) Zero (b) 5 N (c) 4 N (d) 1 N
8. A mass m is attached to a thin wire and whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break when:
(a) inclined at a 60 angle from vertical.
(b) the mass is at the highest point.
(c) the wire is horizontal.
(d) the mass is at the lowest point.
9. A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. The normal force on the motorcycle as it ascends the overbridge will be:
(a) increases. (b) decreases.
(c) remains the same. (d) fluctuates erratically.
10. An object of mass m is held against a vertical wall by applying horizontal force F as shown in the figure. The minimum value of the force F will be: (Consider friction between wall and object.)
 (a) less than mg (b) equal to mg
(a) less than mg (b) equal to mg
(c) greater than mg (d) cannot determine
11. A 100 kg gun fires a ball of 1 kg horizontally from a cliff at a height of 500 m. It falls on the ground at a distance of 400 m from the bottom of the cliff. The recoil velocity of the gun is (g = 10 m/s2)
(a) 0.2 m/s (b) 0.4 m/s
(c) 0.6 m/s (d) 0.8 m/s
12. distance 4r from the center. On doubling the angular velocity of the table, the coin will just slip when the distance from the centre is equal to. coin placed on a rotating table just slips if it is placed at a:
(a) 4r (b) 2r (c) r (d) r/4
13. If the force acting on a system is zero, the quantity which remains constant is:
(a) Force (b) Linear momentum
(c) Speed (d) Kinetic energy
14. A parachutist falls downward with an acceleration of 2 m/s2 at a height of 200 m from the ground. Calculate the up thrust of air if the mass of the parachutist is 60 kg (assume g = 10 m/s2 )
(a) 480 N (b) 620 N (c) 720 N (d) 600 N
15. The variation of momentum with the time of one of the bodies in a two-body collision is shown in fig. The instantaneous force is the maximum corresponding to the point
 (a) P (b) Q
(a) P (b) Q
(c) R (d) S
1. b 2. a 3. c 4. d 5. a 6. c 7. c 8. d 9. a 10. c 11. b 12. c 13. b 14. a 15. c
MCQs on Work, Energy, & Power
- You lift a heavy book from the floor of the room and keep it in the book-shelf having a height 2 m. In this process you take 5 seconds. The work done by you will depend upon
(a) Mass of the book and time taken.
(b) Weight of the book and height of the book-shelf.
(c) Height of the book-shelf and time taken.
(d) Mass of the book, height of the book-shelf and time taken.
- Two springs have their force constant as k1 and k2(k1>k2) . When they are stretched by the same force
(a) No work is done in case of both the springs.
(b) Equal work is done in case of both the springs.
(c) More work is done in case of second spring.
(d) More work is done in case of first spring.
- The force constant of a wire is k and that of another wire is 2k. When both the wires are stretched through same distance, then the work done
(a) W2 = 2W12 (b) W2 = 2W1
(c) W2 = W1 (d) W2 = 0.5W1
- A ball is released from the top of a tower. The ratio of work done by force of gravity in first, second and third second of the motion of the ball is
(a) 1 : 2 : 3 (b) 1 : 4 : 9
(c) 1 : 3 : 5 (d) 1 : 5 : 3
- From an automatic gun a man fires 360 bullet per minute with a speed of 360 km/hour. If each weighs 20 g, the power of the gun is
(a) 100W (b) 600W
(c) 200W (d) 150W
- The heart pushes 1 cc of blood in one second under pressure 20000 N/m2 the power of heart is
(a) 0.02 W (b) 0.4 W
(c) 0.6 W (d) 0.2 W
- A steel ball of radius 2 cm is at rest on a frictionless surface. Another ball of radius 4cm moving at a velocity of 81 cm/sec collides elastically with first ball. After collision the smaller ball moves with speed of
(a) 81 cm/sec (b) 63 cm/sec
(c) 144 cm/sec (d) None of these
- An inelastic ball is dropped from a height of 100 m. Due to earth, 20% of its energy is lost. To what height the ball will rise
(a) 80 m (b) 40 m
(c) 60 m (d) 20 m
- A body of mass M1 collides elastically with another mass M2 at rest. There is maximum transfer of energy when
(a) M1 > M2 (b) M1 < M2
(c) M1 = M2 (d) none of these
- A 50 g bullet moving with velocity 10 m/s strikes a block of mass 950 g at rest and gets embedded in it. The loss in kinetic energy will be
(a) 100% (b) 95%
(c) 5% (d) 50%
- A particle of mass m moving with velocity v strikes a stationary particle of mass 2m and sticks to it. The speed of the system will be
(a) v / 2 (b) 2v
(c) v / 3 (d) 3v
- Two springs have their force constant as k1 and k2(k1>k2) . When they are stretched by the same force
(a) No work is done in case of both the springs.
(b) Equal work is done in case of both the springs.
(c) More work is done in case of second spring.
(d) More work is done in case of first spring.
- The force constant of a wire is k and that of another wire is 2k. When both the wires are stretched through same distance, then the work done
(a) W2 = 2W12 (b) W2 = 2W1
(c) W2 = W1 (d) W2 = 0.5W1
- From a waterfall, water is falling down at the rate of 100 kg/s on the blades of turbine. If the height of the fall is 100 m, then the power delivered to the turbine is approximately equal to
- a) 100 kW (b) 1 kW
(c) 15 kW (d) 150 kW
- A car of mass 1000 kg accelerates uniformly from rest to a velocity of 54 km/hour in 5s. The average power of the engine during this period in watts is (neglect friction)
(a) 200 W (b) 22500 W
(c) 5250 W (d) 2050 W
- An engine develops 10 kW of power. How much time will it take to lift a mass of 200 kg to a height of 40 m.(10 m/s2)
(a) 3 sec (b) 6 sec
(c) 8 sec (d) 5 sec
- In an inelastic collision, what is conserved
(a) Kinetic energy (b) Momentum
(c) Both (a) and (b) (d) Neither (a) nor (b)
- Two springs of spring constants 1500 N/m and 3000 N/m respectively are stretched with the same force. They will have potential energy in the ratio
(a) 4 : 1 (b) 1 : 4
(c) 2 : 1 (d) 1 : 2
- A spring 40 mm long is stretched by the application of a force. If 10 N force required to stretch the spring through 1 mm, then work done in stretching the spring through 40 mm is
(a) 84 J (b) 68 J
(c) 23 J (d) 8 J
- Work done in raising a box depends on
(a) How fast it is raised (b) The strength of the man
(c) The height by which it is raised (d) None of the above
- b 2. c 3. b 4.c 5. b 6. a 7. c 8.a 9. c 10. b 11.c 12.c 13.b 14. a 15. b 16. c 17.b 18.c 19.d 20.c .
MCQs on Rotational Motion
- A man hangs from a rope attached to a hot-air balloon. The man’s mass is greater than the mass of the balloon and its contents. The system is stationary in the air. If the man now climbs up to the balloon using the rope, the centre of mass of the “man plus balloon” system will:
(a) remain stationary.
(b) move up.
(c) move down.
(d) first moves up and then return to its initial position.
- A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is:
(a) zero (b) increasing with x
(c) decreasing with x (d) remaining constant
- The law of conservation of angular momentum is valid when:
(a) The net force is zero and the net torque is non-zero.
(b) The net force is non-zero and the net torque is non-zero.
(c) Net force may or may not be zero and net torque is zero.
(d) Both force and torque must be zero.
- A disc and a solid sphere of the same radius but different masses roll off on two inclined planes of the same altitude and length. Which one of the two objects gets to the bottom of the plane first?
(a) Sphere (b) Both reach at the same time
(c) Depends on their masses (d) Disc
- A drum of radius R and mass M rolls down without slipping along an inclined plane of angle θ. The frictional force:
(a) Decreases the rotational and translational motion.
(b) Dissipates energy as heat.
(c) Decreases the rotational motion.
(d) Converts translational energy to rotational energy.
- Which of the following will not be affected if the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping mass constant?
(a) Moment of inertia (b) Angular momentum
(c) Angular velocity (d) Rotational kinetic energy
- A solid homogenous sphere is moving on a rough horizontal surface, partially rolling and partially sliding. During this motion of this sphere:
(a) The total kinetic energy is conserved.
(b) The angular momentum of the sphere about the point of contact is conserved.
(c) Only the rotational kinetic energy about the centre of mass is conserved.
(d) Angular momentum about the centre of mass is conserved.
- A ring and a disc with the same moment of inertia roll along a plane surface at the same speed. If Er be the rotational kinetic energy of the ring and Ed be that of the disc, then:
(a)Er > Ed (b) Er < Ed
(c)Er = Ed (d) The relation depends upon the radii of the ring & disc
- Two gear wheels that are meshed together have radii of 0.50 cm and 0.15 cm. The number of revolutions made by the smaller one when the larger one goes through 3 revolutions is:
(a) 5 revolutions (b) 20 revolutions
(c) 10 revolution (d) 1 revolutions
- A disc rolls without slipping, climbs on a rough incline, and comes back. During the motion on the incline,

(a) Friction is downward during the upward journey.
(b) Friction is upward during the upward journey.
(c) Friction is zero.
(d) Information is insufficient to predict.
- A rigid body rotates with an angular momentum of L. . If its kinetic energy is halved, the angular momentum becomes
(a) L (b) L/2
(c) 2L (d) L/√2
- If the radius of the earth is suddenly contracted to half of its present value, then the duration of the day will be of
(a) 6 hours
(b) 12 hours
(c) 18 hours
(d) 24 hours
- A man hangs from a rope attached to a hot-air balloon. The man’s mass is greater than the mass of the balloon and its contents. The system is stationary in the air. If the man now climbs up to the balloon using the rope, the centre of mass of the “man plus balloon” system will:
(a) remain stationary.
(b) move up .
(c) move down .
(d) first moves up and then return to its initial position.
- A string of negligible thickness is wrapped several times around a cylinder kept on a rough horizontal surface. A man standing at a distance l from the cylinder holds one end of the string and pulls the cylinder towards him. There is no slipping anywhere. The length of the string that passed through the hand of the man while the cylinder reaches his hands is-[Assume radius of the cylinder is negligible compared to length ‘l’ of string]

(a) l (b) 2l
(c) 3l (d) 4l
- The moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc is maximum about an axis perpendicular to the disc and passing through:
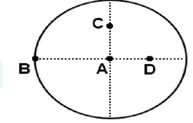 (a) B (b) A
(a) B (b) A
(c) D (d) C
1. a 2. d 3. c 4. a 5. d 6. b 7. b 8. d 9. c 10. b 11. d 12. a 13. a 14. b 15. c
MCQs on Gravitation
Newton Laws of Gravitation
Acceleration due to gravity
- Gravitational mass is proportional to gravitational
(a) Field (b) Force (c) Intensity (d) All of these
- The distance of the centres of moon and earth is D. The mass of earth is 81 times the mass of the moon. At what distance from the centre of the earth, the gravitational force will be zero
(a) 2D/3 (b) D/2 (c) 9D/10 (d) 4D/3
- Mass M is divided into two parts xM and (1 – x)M . For a given separation, the value of x for which the gravitational attraction between the two pieces becomes maximum is
(a) ½ (b) 1 (c) 3/5 (d) 2
- The force of gravitation is
(a) Repulsive (b) Electrostatic
(c) Conservative (d) Non-conservative
- Two sphere of mass m and M are situated in air and the gravitational force between them is F. The space around the masses is now filled with a liquid of specific gravity 3. The gravitational force will now be
(a) F (b) F/2 (c) 3F (d) F/6
- When a body is taken from the equator to the poles, its weight
(a) Remains constant
(b) Increases
(c) Decreases
(d) Increases at N-pole and decreases at S-pole
- A body of mass m is taken to the bottom of a deep mine. Then
(a) Its mass increases (b) Its mass decreases
(c) Its weight increases (d) Its weight decreases
- The mass of the earth is 81 times that of the moon and the radius of the earth is 3.5 times that of the moon. The ratio of the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the moon to that at the surface of the earth is
(a) 0.15 (b) 0.03 (c) 1.5 (d) 4
- If the earth suddenly shrinks (without changing mass) to half of its present radius, the acceleration due to gravity will be
(a) g/2 (b) 4g (c) g/3 (d) 3g
- At what height from the ground will the value of ‘g’ be the same as that in 10 km deep mine below the surface of earth
(a) 30 km (b) 20 km (c) 15 km (d) 10 km
Gravitation Potential, Energy and Escape Velocity
Motion of Satellite
- A body of mass m rises to height h = R/5 from the earth’s surface, where R is earth’s radius. If g is acceleration due to gravity at earth’s surface, the increase in potential energy is
(a) mgh (b) 6/5 mgh (c) 5/6 mgh (d) 6/7 mgh
A rocket is launched with velocity 10 km/s. If radius of earth is R, then maximum height attained by it will be
(a) 8R (b) 6R (c) 4R (d) 8R
- A body is projected vertically upwards from the surface of a planet of radius R with a velocity equal to half the escape velocity for that planet. The maximum height attained by the body is
(a) R/3 (b) R/5 (c) R/6 (d) R/7
- In some region, the gravitational field is zero. The gravitational potential in this region
(a) Must be variable (b) Must be constant
(c) Cannot be zero (d) Must be zero
- The velocity with which a projectile must be fired so that it escapes earth’s gravitation does not depend on
(a) Mass of the earth (b) Mass of the projectile
(c) Radius of the projectile’s orbit (d) Gravitational constant
- The ratio of the K.E. required to be given to the satellite to escape earth’s gravitational field to the K.E. required to be given so that the satellite moves in a circular orbit just above earth atmosphere is
(a) One (b) Half (c) Two (d) Infinity
17. The period of a satellite in a circular orbit around a planet is independent of
(a) The mass of the planet (b) The radius of the planet
(c) The mass of the satellite (d) All (a), (b) and (c)
18. The time period of a geostationary satellite is
(a) 24 hours (b) 12 hours (c) 365 days (d) One month
- If Gravitational constant is decreasing in time, what will remain unchanged in case of a satellite orbiting around earth
(a) Time period (b) Orbiting radius
(c) Tangential velocity (d) Angular velocity
- If satellite is shifted towards the earth. Then time period of satellite will be
(a) Increase (b) Decrease
(c) Unchanged (d) Nothing can be said
1. d 2. c 3. a 4. c 5. a 6. b 7. d 8. a 9. b 10. b 11. c 12. c 13. a 14. b 15. b 16. c 17. a 18. a 19. c 20. b
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
- The period of a satellite in a circular orbit of radius R is T, the period of another satellite in a circular orbit of radius 4R is (a) 4T (b) T/4 (c) 8T (d) T/8
- Orbit of a planet around a (a) A circle (b) An ellipse (c) A parabola (d) A straight line
- The orbital speed of Jupiter is (a) Greater than the orbital speed of earth. (b) Less than the orbital speed of earth. (c) Equal to the orbital speed of earth. (d) Zero.
- The period of revolution of planet A around the sun is 8 times that of B. The distance of A from the sun is how many times greater than that of B from the sun (a) 3 (b) 7 (c) 4 (d) 6
- If the radius of earth’s orbit is made 1/4, the duration of an year will become (a) 6 times (b) 2 times (c) 1/8 times (d) 1/4 times _____________________________________________________
Assertion and Reason
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion (b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. (c) If assertion is true but reason is false. (d) If the assertion and reason both are false. (e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
- Assertion : Gravitational force between two particles is negligibly small compared to the electrical force. Reason : The electrical force is experienced by charged particles only.
7. Assertion : If a pendulum is suspended in a lift and lift is falling freely, then its time period becomes infinite. Reason : Free falling body has acceleration equal to acceleration due to gravity.
8. Assertion : The time period of geostationary satellite is 24 hours. Reason : Geostationary satellite must have the same time period as the time taken by the earth to complete one revolution about its axis.
- Assertion : A person sitting in an artificial satellite revolving around the earth feels weightless. Reason : There is no gravitational force on the satellite.
- Assertion : Gravitational potential of earth at every place on it is negative.
Reason : Everybody on earth is bound by the attraction of earth.
11 Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. g is maximum | 1. At the moon |
| B. g is minimum | 2. At the pole |
| C. g is zero | 3. At the equator |
| D. g is 1/6 of the original value | 4. At the center of the earth |
(a) A – 1, B – 2, C – 3, D – 4
(b) A – 2, B – 3, C – 4, D – 1
(c) A – 4, B – 3, C – 2, D – 1
(d) A – 4, B – 2, C – 3, D – 1
- Match the following columns.
| . Column I | Column II |
| A.Orbital velocity of a satellite near Earth’s surface | (i) 2.38 kms-1 |
| B. Escape velocity on Earth’s surface | (ii) 7.92 kms-1 |
| C. Escape velocity at moon | (iii) 11.2 kms-1 |
(a) A – (ii) , B – (iii) , C – (i)
(b) A – (iii) , B – (i) , C – (ii)
(c) A – (i) , B – (ii) , C – (iii)
(d) A – (ii) , B – (ii) , C – (iii)
1. c 2. b 3. b 4. c 5. c 6. b 7. b 8. b 9. c 10. a 11. b 12. a |
MCQs on Properties of Solids & Liquids
Young’s Modulus and Breaking Stress
Bulk Modulus
- The increase in length is l of a wire of length L by the longitudinal stress. Then the stress is proportional to
(a) L/l (b) l/L (c) l x L (d) l 2 x L
- The ratio of the lengths of two wires A and B of same materialis 1 : 2 and the ratio of their diameter is 2 :1. They are stretched by the same force, then the ratio of increase in length will be
(a) 3 : 1 (b) 1 : 6 (c) 1 : 8 (d) 7 : 1
- The Young’s modulus of a wire of length L and radius r is Y N/m2. If the length and radius are reduced to L/2 and r/2, then its Young’s modulus will be
(a) Y/2 (b) 3Y (c) 2Y (d) 5Y
- Hook’s law defines
(a) Stress (b) Strain
(c) Modulus of elasticity (d) Elastic limit
- A and B are two wires. The radius of A is twice that of B. They are stretched by some load. Then the stress on B is
(a) Equal to that on A (b) Four times that on A
(c) Two times that on A (d) Half that on A
- The only elastic modulus that applies to fluids is
(a) Young’s modulus (b) Shear modulus
(c) Modulus of rigidity (d) Bulk modulus
- If the volume of the given mass of a gas is increased four times, the temperature is raised from 27°C to 127°C. The elasticity will become
(a) 2 times (b) 1/2 times (c) 4 times (d) 1/3 times
- In the three states of matter, the elastic coefficient can be
(a) Young’s modulus (b) Coefficient of volume elasticity
(c) Modulus of rigidity (d) Poisson’s ratio
- The Bulk modulus for an incompressible liquid is
(a) Zero (b) Unity
(c) Infinity (d) Between 0 to 1
Rigidity Modulus
- Modulus of rigidity of diamond is
(a) Too less (b) Greater than all matters
(c) Less than all matters (d) Zero
- The reason for the change in shape of a regular body is
(a) Volume stress (b) Shearing strain
(c) Longitudinal strain (d) Metallic strain
- When a spiral spring is stretched by suspending a load on it, the strain produced is called
(a) Shearing (b) Longitudinal
(c) Volume (d) Transverse
- Modulus of rigidity of a liquid
(a) Non-zero constant (b) Infinite
(c) Zero (d) None of these
- When shearing force is applied on a body, then the elastic potential energy is stored in it. On removing the force, this energy
(a) Converts into kinetic energy (b) Converts into heat energy
(c) Remains as potential energy (d) None of the above
MCQs on Thermodynamics
Thermometry
Thermal Expansion
- On the Celsius scale the absolute zero of temperature is at
(a) 0°C (b) – 32°C (c) 100°C (d) – 273.15°C
- The absolute zero is the temperature at which
(a) Water freezes (b) All substances exist in solid state
(c) Molecular motion ceases (d) None of the above
- The gas thermometers are more sensitive than liquid
thermometers because
(a) Gases expand more than liquids
(b) Gases are easily obtained
(c) Gases are much lighter
(d) Gases do not easily change their states
- On centigrade scale the temperature of a body increases by 30
degrees. The increase in temperature on Fahrenheit scale is
(a) 50° (b) 40° (c) 30° (d) 54°
- On which of the following scales of temperature, the temperature is never negative
(a) Celsius (b) Fahrenheit (c) Reaumur (d) Kelvin
- When a copper ball is heated, the largest percentage increase
will occur in its
(a) Diameter (b) Area (c) Volume (d) Density
- A solid ball of metal has a concentric spherical cavity within
- If the ball is heated, the volume of the cavity will
(a) Increase (b) Decrease
(c) Remain unaffected (d) None of these
- Water has maximum density at
(a) 0°C (b) 32°F (c) – 4°C (d) 4°C
- A litre of alcohol weighs
(a) Less in winter than in summer
(b) Less in summer than in winter
(c) Some both in summer and winter
(d) None of the above
- A beaker is completely filled with water at 4°C. It will
overflow if
(a) Heated above 4°C
(b) Cooled below 4°C
(c) Both heated and cooled above and below 4°C respectively
(d) None of the above
First Law of Thermodynamics
Isothermal Process
- The internal energy of an ideal gas depends upon
(a) Specific volume (b) Pressure
(c) Temperature (d) Density
- The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of
(a) Momentum (b) Energy (c) Mass (d) Temperature
- Work done on or by a gas, in general depends upon the
(a) Initial state only
(b) Final state only
(c) Both initial and final states only
(d) Initial state, final state and the path
- If heat given to a system is 6 kcal and work done is 6 kJ.
Then change in internal energy is
(a) 19.1 kJ (b) 12.5 kJ (c) 25 kJ (d) Zero
- Temperature is a measurement of coldness or hotness of an object.This definition is based on
(a) Zeroth law of thermodynamics.
(b) First law of thermodynamics.
(c) Second law of thermodynamics.
(d) Newton’s law of cooling.
- In an isothermal expansion
(a) Internal energy of the gas increases.
(b) Internal energy of the gas decreases.
(c) Internal energy remains unchanged.
(d) Average kinetic energy of gas molecule decreases.
- In isothermal expansion, the pressure is determined by
(a) Temperature only
(b) Compressibility only
(c) Both temperature and compressibility
(d) None of these
- The specific heat of a gas in an isothermal process is
(a) Infinite (b) Zero (c) Negative (d) Remains constant
- A thermodynamic process in which temperature T of the system remains constant though other variable P and V may change, is called
(a) Isochoric process (b) Isothermal process
(c) Isobaric process (d) None of these
- When heat is given to a gas in an isothermal change, the
result will be
(a) External work done
(b) Rise in temperature
(c) Increase in internal energy
(d) External work done and also rise in temp.
Adiabatic Process
Isobaric and Isochoric Processes
21. The work done in an adiabatic change in a gas depends only on
(a) Change is pressure (b) Change is volume
(c) Change in temperature (d) None of the above
22. In adiabatic expansion
(a) DU = 0 (b) DU = negative
(c) DU = positive (d) DW = zero
23. Two identical samples of a gas are allowed to expand
(i) isothermally (ii) adiabatically. Work done is
(a) More in the isothermal process
(b) More in the adiabatic process
(c) Neither of them
(d) Equal in both processes
24. When a gas expands adiabatically
(a) No energy is required for expansion.
(b) Energy is required and it comes from the wall of the
container of the gas.
(c) Internal energy of the gas is used in doing work.
(d) Law of conservation of energy does not hold.
25. A cycle tyre bursts suddenly. This represents an
(a) Isothermal process (b) Isobaric process
(c) Isochoric process (d) Adiabatic process
26. Which of the following is correct in terms of increasing work done for the same initial and final state
(a) Adiabatic < Isothermal < Isobaric
(b) Isobaric < Adiabatic < Isothermal
(c) Adiabatic < Isobaric < Isothermal
(d) None of these
27. Entropy of a thermodynamic system does not change when
this system is used for
(a) Conduction of heat from a hot reservoir to a cold reservoir.
(b) Conversion of heat into work isobarically.
(c) Conversion of heat into internal energy isochorically.
(d) Conversion of work into heat isochorically.
28. In an isochoric process if T1 = 270 C and T2 = 1270 C then
P1/ P2 will be equal to
(a) 9 / 59 (b) 2 / 3 (c) 3 / 4 (d) None of these
29. In a cyclic process, work done by the system is
(a) Zero.
(b) Equal to heat given to the system.
(c) More than the heat given to system.
(d) Independent of heat given to the system.
30. Match the Column
Column I Column II |
(A)Isothermal (p) ΔQ = 0 |
(B)Isobaric (q) Volume constant |
(C)Isochoric (r) Pressure constant |
(D)Adiabatic (s) Temperature constant |
(a) A – s, B – r, C – q, D – p (b) A – q, B – s, C – r, D – p
(c) A – p, B – r, C – q, D – s (d) A – r, B – s, C – p, D -q
1. b 2. c 3. a 4. d 5. d 6. c 7. a 8. d 9. b 10. c11. c 12. b 13 d 14. a 15. a 16. c 17. b 18. a 19. b 20. d 21. c 22. b 23. a 24. a 25. d 26. a 27. a 28. c 29. b 30. a
MCQs on Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Every gas (real gas) behaves as an ideal gas
(a) At high temperature and low pressure.
(b) At low temperature and high pressure.
(c) At normal temperature and pressure.
(d) None of the above.
- Boyle’s law holds for an ideal gas during
(a) Isobaric changes (b) Isothermal changes
(c) Isochoric changes (d) Isotonic changes
- Molecules of a gas behave like
(a) Inelastic rigid sphere.
(b) Perfectly elastic non-rigid sphere.
(c) Perfectly elastic rigid sphere.
(d) Inelastic non-rigid sphere.
- A gas is enclosed in a closed pot. On keeping this pot in a train
moving with high speed, the temperature of the gas
(a) Will increase.
(b) Will decrease.
(c) Will remain the same.
(d) Will change according to the nature of the gas.
- The ratio of two specific heats Cp / Cv of CO is
(a) 1.33 (b) 1.40 (c) 1.29 (d) 1.66
- When the temperature of a gas is raised from 27°C to 90°C, the percentage increase in the r.m.s. velocity of the molecules will be
(a) 10% (b) 15% (c) 20% (d) 17.5%
- The volume of a gas at pressure 21 x 104 N/m2 and temperature 27°C is 83 litres. If R = 8.3 J/mol/K, then the quantity of gas in gm-mole will be
(a) 15 (b) 42 (c) 7 (d) 14
- A pressure cooker contains air at 1 atm and 30°C. If the safety value of the cooler blows when the inside pressure ≥ 3 atm, then the maximum temperature of the air, inside the cooker can be
(a) 90°C (b) 636°C (c) 909°C (d) 363°C
- Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will
(a) increase.
(b) decrease.
(c) remain the same.
(d) decrease for some, while the increase for others.
10. The equation of state for 5g of oxygen at a pressure P and temperature T, when occupying a volume V, will be (where R is the gas constant) :
(a) PV = 5 RT (b) PV = (5/2) RT
(c) PV = (5/16) RT (d) PV = (5/32) RT
11. If the mean free path of atoms is doubled , then the pressure of the gas will become
(a) P/4 (b) P/2 (c)P/8 (d) P
12. Heat is associated with:
(a)kinetic energy of random motion of molecules.
(b)kinetic energy of orderly motion of molecules.
(c) total kinetic energy of random and orderly motion of molecules.
(d) kinetic energy of random motion in some cases and kinetic energy of orderly motion in other cases.
13. If VH, VN and VO denote the root-mean square and velocities of molecules of hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen respectively at a given temperature, then
(a) VN > VO > VH (b) VH > VN > VO
(c) VO > VN > VH (d) VO > VH > VN
1. a 2. b 3. c 4.c 5. c 6. a 7. c 8. b 9. C 10. d 11. B 12. a 13. b
- Calculate the amplitude for a SHM using the equation
x = 3sin2pt + 4cos3pt
(a) 3 (b) 5 (c) 4 (d) 7
- What is the phase difference between the prongs of the tuning fork
(a) 5π (b) π (c) 2π (d) 3π
- Which of the following does not exhibit polarization
(a) Longitudinal wave in a gas
(b) Transverse wave in a gas
(c) Neither (a) nor (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
- A particle executes S.H.M of amplitude A. At what distance from the mean position is its kinetic energy equal to its potential energy?
(a) 0.51 A (b) 0.61 A (c) 0.71 A (d) 0.81 A
- The energy of a simple harmonic motion depend upon:-
(a) ⍵ (b) 1/⍵2 (c) A2 (d) 1/A2
- What is the ratio of potential energy to kinetic energy of a body executing simple harmonic motion when the displacement is equal to one-third of the amplitude?
(a) 1:8 (b) 8:1 (c) 1:3 (d) 3:4
7. Time period of simple pendulum inside the satellite orbiting earth is
(a) Zero (b) 2T (c) T (d) Infinite
8. The length of a simple pendulum is increased then the time period will-
(a) Decrease (b) increase
(c) remain same (d) Both (a) and (b)
9. F= -kx is the force on a particle of mass ‘m’ undergoing SHM. What is the relationship between x and in terms of angular frequency?
(a) k = ω2 ω (b) k = m√ω
(c) m = k/ω2 (d) m = k2/ω
10. The observer perceives a sound coming from a source that is moving away from the stationary observer. Determine the sound’s frequency.
(a) It’s been halved. (b) It hasn’t changed.
(c) It extends to infinity. (d) It’ll be doubled.
1. a 2. b 3. a 4.c 5. c 6. a 7. d 8. b 9. C 10. a
- Two small conducting sphere of equal radius have charges + 1 c and – 2 c respectively and placed at a distance d from each other experience force F1. If they are brought in contact and separated to the same distance, they experience force F2. The ratio of F1 to F2 is ……….
(a) –8 : 1 (b) 1 : 2 (c) 1 : 8 (d) –2 : 1
- The force between two charges 0.06 m apart is 5 N. If each charge is moved towards the other by 0.01 m, then the force between them will become:
(a) 7.20 N (b) 11.25 N (c) 22.50 N (d) 45.00 N
- Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and carrying equal charges in them repel each other with a force F when kept apart at some distance. A third spherical conductor having same radius as that of B but uncharged is brought in contact with B, then brought in contact with C and finally removed away from both. The new force of repulsion between B and C is
(a) F/4 (b) 3 F/4 (c) F/8 (d) 3 F/8
- The electrostatic field due to a charged conductor just outside the conductor is
(a) zero and parallel to the surface at every point inside the conductor.
(b) zero and is normal to the surface at every point inside the conductor.
(c) parallel to the surface at every point and zero inside the conductor.
(d) normal to the surface at every point and zero inside the conductor.
- An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a sphere. Which of the following is correct?
(a) The electric flux through the sphere is zero.
(b) The electric field is zero at every point on the sphere.
(c) The electric field is zero at every point inside the sphere.
(d) The electric field is uniform inside the sphere.
- An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward-directed electric field E. The direction of the electric field is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest through the same vertical distance h. The fall time of the electron in comparison to the fall time of the proton is:
(a) smaller. (b) 5 times greater.
(c) 10 times greater. (d) equal.
- An electric dipole is kept in a uniform electric field such that the dipole moment is not collinear with the electric field. It experiences:
(a) a force and torque. (b) a force but no torque.
(c) a torque but no force. (d) neither a force nor a torque.
- 5 C of charge is passed through a battery in a given time. The plates of the battery are maintained at a potential difference of 12 V. The work done by the battery is:
(a) 120 J (b) 60 J (c) 30 J (d) 15 J
- An electron enters an electric field with its velocity in the direction of the electric lines of force. Then:
(a) the path of the electron will be a circle.
(b) the path of the electron will be a parabola.
(c) the velocity of the electron will decrease.
(d) the velocity of the electron will increase.
- The effective capacity of the network between terminals A and B is:

(a) 6 µF (b) 20 µF
(c) 3 µF (d) 10 µF
- The electrostatic force between the metal plates of an isolated parallel plate capacitor C having a charge Q and area A is:
(a) independent of the distance between the plates.
(b) linearly proportional to the distance between the plates.
(c) proportional to the square root of the distance between the plates.
(d) inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
12. Work done to carry a negatively charged body in direction of the electric field: (assuming no other force is acting on the body)
(a) is always negative. (b) maybe negative.
(c) is always positive. (d) maybe zero.
- How much kinetic energy will be gained by an α particle in going from a point at 70 V to another point at 50 V?
(a) 40 eV (b) 40 keV (c) 0 eV (d) 40 MeV
- Eight equals charged tiny drops are combined to form a big drop. If the potential on each drop is 10V then potential of big drop will be
(a) 40V (b) 10V (c) 30V (d) 20V
- A parallel plate capacitor having cross-sectional area A and separation d has air in between the plates. Now an insulating slab of the same area but thickness d/2 is inserted between the plates as shown in the figure having dielectric constant K(=4). The ratio of new capacitance to its original capacitance will be?
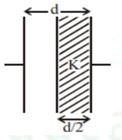
(a) 6:5 (b) 2:1 (c) 4:1 (d) 8:5
1. a 2. b 3. d 4. d 5. a 6. a 7. c 8. b 9. c 10. a11. a 12. c 13. a 14. a 15. d
MCQs on Current Electricity
- If the potential difference across ends of a metallic wire is doubled, the drift velocity of charge carriers will become:
(a) Double (b) Halved
(c) Four times (d) One-fourth
- The current in a wire varies with time according to the relation i= (3+2t)A. The amount of charge passing a cross section of the wire in the time interval t=0 to t=4.0 sec would be (where t is time in seconds)
(a) 34 C (b) 30.5 (c) 28 C (d) 82 C
- Across a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section, a constant potential difference is applied. The quantity which remains constant along the conductor is :
(a) current density (b) current
(c)drift velocity (d) electric field
- An electric kettle takes 4 A current at 220 V. How much time will it take to boil 1 kg of water from temperature 20oC? The temperature of boiling water is 100 °C.
(a) 8.3 min (b) 6.3 min (c) 12.6 min (d) 4.2 min
- Suppose a voltmeter of resistance 660 reads the voltage of a very old cell to be 1.32 volt while a potentiometer reads its voltage to be 1.44 volt. The internal resistance of the cell is:
(a) 30 Ω (b) 40 Ω (c) 60 Ω (d) 0.6 Ω
- Two solid conductors are made up of the same material, have the same length and same resistance. One of them has a circular cross-section of area A1 and the other one has a square cross-section of area A2 . The ratio A1/A2 is:
(a) 1.5 (b) 1 (c) 0.8 (d) 2
- 12 cells each having the same emf are connected in series with some cells wrongly connected. The arrangement is connected in series with an ammeter and two similar cells which are in series. Current is 3 A when cells and battery aid each other and is 2 A when cells and battery oppose each other. The number of cells wrongly connected is
(a) 4 (b) 5 (c) 6 (d) 1
- The current passes through a wire of variable cross-section in steady-state as shown. Then incorrect statement is:

(a) Current density increases in the direction of the current.
(b) Potential increases in the direction of the current.
(c) Electric field increases in the direction of the current.
(d) Drift speed increases in the direction of the current.
- A constant voltage is applied between the two ends of a uniform metallic wire. Some heat is developed in it. The heat developed is doubled if:
(a) both the length and the radius of the wire are halved.
(b) the length of the wire is doubled.
(c) the radius of the wire is doubled.
(d) both the length and the radius of the wire are doubled.
- If voltage across a bulb rated 220 V-100 W drops by 2.5% of its rated value, the percentage of the rated value by which the power would decrease is :
(a) 20% (b) 2.5% (c) 5% (d) 10%
The voltmeters are connected as shown.

A potential difference has been applied between A and B. On closing the switch S, readings of voltmeter:
(a) V1 increases. (b) V2 and V3 both increases.
(c) V2 decreases. (d) one of V2 , V3 increases and the other decreases.
- What is the ratio of currents flowing in the resistors x and y of resistance 10 each?

(a) 2.5 (b) 1.5 (c) 1 (d) 0.5
- The resistances of the four arms P, Q, R and S in a Wheatstone’s bridge are 10-ohm, 30-ohm, 30 ohm and 90 ohms, respectively. The e.m.f. and internal resistance of the cell are 7 Volt and 5 ohms respectively. If the galvanometer resistance is 50 ohms, the current drawn from the cell will be :
(a) 0.2 A (b) 0.1 A (c) 2.0 A (d) 1.0 A
- Two cities are 150 km apart. Electric power is sent from one city to another city through copper wires. The fall of potential per km is 8 volt and the average resistance per km is 0.5. The power loss in the wire is:
(a) 19.2 W (b) 19.2 kW (c) 19.2 J (d) 12.2 kW
- The terminal potential difference of a cell is greater than its emf when
(a) A battery of less emf is connected in its series.
(b) A battery of higher emf is connected in its series.
(c) A battery of higher emf is connected in its parallel.
(d) A battery of less emf is connected in its parallel.
1. a 2.c 3. b 4. b 5. c 6. b 7. d 8. b 9. d 10. c 11. a 12. c 13. a 14. b 15. c
MCQs on Magnetic effect of current and magnetism
- A circular loop of radius R carrying current I lie in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The total magnetic flux through the x-y plane is:
(a) directly proportional to I. (b) directly proportional to R.
(c) directly proportional to R2. (d) zero.
- An inductor is connected to a direct voltage source through a switch. Then:
(a) a very large emf is induced in inductor when switch is closed.
(b) a Large emf is induced when switch is opened.
(c) a large emf is induced whether switch is closed or opened.
(d) no emf is induced whether switch is closed or opened.
- A metallic ring is attached to the wall of a room. When the north pole of a magnet is brought near to it, the induced current in the ring will be:

(a) first clockwise and then anticlockwise.
(b) in the clockwise direction.
(c) in the anticlockwise direction.
(d) first anticlockwise then clockwise.
- A coil has 1,000 turns and 500 cm2 as its area. The plane of the coil is placed at right angles to a magnetic field of 2 × 10−5 Wb/m2 . The coil is rotated through 180° in 0.2 seconds. The average e.m.f. induced in the coil, in milli-volts, is.
(a) 5 (b) 10 (c) 15 (d) 20
- Eddy currents are induced when:
(a) a metal block is kept in a changing magnetic field.
(b) a metal block is kept in a uniform magnetic field.
(c) a coil is kept in a uniform magnetic field.
(d) current is passed in a coil.
- Two circular coils can be arranged in any of the three situations shown in the figure. Their mutual inductance will be:

(a) maximum in the situation (A). (b) maximum in the situation (B).
(c) maximum in the situation (C). (d) the same in all situations.
- With the decrease of current in the primary coil from 2 A to zero in 0.01s, the e.m.f. generated in the secondary coil is 1000 V. The mutual inductance of the two coil is?
(a) 1.25 H (b) 2.50 H (c) 5.00 H (d) 10.00 H
- Work done in increasing the current through a solenoid from 0 to 2 A is 20 J. Work done in increasing the current from 4 to 6 A is
(a) 100 J (b) 60 J
(c) 80 J (d) 120 J
- In a circuit with a coil of resistance 2 ohms, the magnetic flux changes from 2.0 Wb to 10.0 Wb in 0.2 second. The charge that flows in the coil during this time is
(a) 5.0 coulomb (b) 4.0 coulomb
(c) 1.0 coulomb (d) 0.8 coulomb
- In a uniform magnetic field, a ring is rotating about its axis which is parallel to the magnetic field and the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The induced electric field in the ring:
(a) is zero.
(b) depends on the radius of the ring.
(c) depends on the nature of the material of the ring.
(d) depends on the product of the magnetic field and speed.
- A short magnet is allowed to fall along the axis of a horizontal metallic ring. Starting from rest, the distance fallen by the magnet in one second may be
(a) 3 m (b) 5 m
(c) 6 m (d) 4 m
- The dimensions of inductance are:
(a) [MLT−2A−2] (b) [ML2T−2A– 2]
(c) [ML2T−2A−1] (d) [ML2T−2A2]
- A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
(a) 45 Wb (b) 65 Wb
(c) 30 Wb (d) 40 Wb
- A series combination of inductance (L) and resistance (R) is connected to a battery of emf E. The final value of current depends on
(a) L and R (b) E and R
(c) E and L (d) E, L, and R
- A bar magnet is made to fall through a long surface copper tube. The speed (v) of the magnet as a function of time (t) is best represented by

(a) a (b) b (c) c (d) d
1. d 2.b 3. c 4. b 5. a 6. a 7. c 8. a 9. b 10. a 11. d 12. b 13. c 14. b 15. d
MCQs on Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Currents
- Dimensional formula of magnetic flux is:
(a) [M L2 T−2 A−1] (b) [M L1 T−1 A−2]
(c) [M L2 T−3 A−1] (d) [M L−2 T−2 A−2]
2. A wire loop is rotated in a magnetic field. The frequency of change of direction of the induced e.m.f. is:
(a) once per revolution. (b) four times per revolution.
(c) six times per revolution. (d) twice per revolution.
3. A coil of resistance 20 ohm and inductance 5H has been connected to a 200 V battery. The maximum energy stored in the coil is
(a) 250 J (b) 125 J (c) 500 J (d) 100 J
4. Alternating current cannot be measured by dc ammeter because, (a) ac cannot pass through dc ammeter .
(b) Average value of complete cycle is zero .
(c) ac is virtual .
(d) ac changes its direction.
5. In the transmission of a.c. power through transmission lines, when the voltage is shapped up n times, the power loss in transmission,
(a) increase n times. (b) Increase n2 times.
(c) Decrease n times. (d) Decrease n2 times.
6. A choke coil has.
(a) High inductance and low resistance.
(b) High inductance and high resistance.
(c) Low inductance and high resistance.
(d) Low inductance and low resistance.
7. The power factor of a good choke coil is
(a) Nearly zero (b) Exactly zero (c) Nearly one (d) Exactly one
8. For high frequency, a capacitor offers
(a) More reactance (b) Less reactance
(c) Zero reactance (d) infinite reactance
9. A coil having area 2m2 is placed in a magnetic field which changes from 1 wb /m2 to 4 wb/m2 in an interval of 2 second. The emf induced in the coil of single turn is….
(a) 4 v (b) 3 v (c) 1.5 v (d) 2 v
10. In circular coil. when no. of turns is doubled & resistance becomes half of the initial then inductance becomes….
(a) 4 times (b) 2 times (c) 8 times (d) No change
11. Two identical circular loops of metal wire are lying on a table near to each other without touching. Loop A carries a current which increasing with time. In response the loop B…….
(a) Is attracted by loop A. (b) rotates about its centre of mass.
(c) Is repelled by loop A. (d) remains stationary.
12. A step down transformer is connected to main supply 200 V to operate a 6V, 30 w bulb. The current in primary is ….
(a) 3A (b) 1.5 A (c) 0.3 A (d) 0.15 A
13. The time constant of a LR circuit is 20 ms The circuit is connected at t = 0 and the steady state current is found to be 4A. Find the current at 80 ms.
(a) 0.98 A (b) 1 A (c) 0.44 A (d) 0.88 A
14. A lamp consumes only 50% of peak power in an ac circuit. What is the phase difference between the applied voltage and the circuit current.
(a) π/4 (b) π/8 (c) π/6 (d) π/2
15. An ideal transformer has 1:25 turn ratio. The peak value of the ac is 28 V. The rms ms secondary voltage is nearest to……
(a) 50 V (b) 70 V (c) 100 V (d) 40 V
1. a 2.d 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. a 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. b 13. d 14. b 15. a
MCQs on Electromagnetic Waves
- In an electric circuit, there is a capacitor of reactance 100 connected across the source of 220V. The rms value of displacement current will be:
(a) 3.2 A (b) 0.22 A (c) 2.2 A (d) 2.4 A
2. A variable frequency AC source is connected to a capacitor. Then on increasing the frequency
(a) Both conduction current and displacement current will increase.
(b) Both conduction current and displacement current will decrease.
(c) Conduction current will increase and displacement will decrease.
(d) Conduction current will decrease and displacement currentwill increase.
3. The most penetrating radiation out of the following is:
(a) x-rays (b) β-rays (c) α-rays (d) γ-rays
4. In an electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillated sinusoidally with amplitude 48 Vm-1 , the RMS value of the oscillating magnetic field will be :
(a) 1. 6 × 10−8 T (b) 1. 6 × 10−9 T
(c) 144 × 10−8 T (d) 11. 3 × 10−8 T
5. In an electromagnetic wave in free space, the root mean square value of the electric field is Erms = 6V/m. The peak value of the magnetic field is:
(a) 2.83 × 10−8 T (b) 0. 70 × 10−8 T
(c) 2.3 × 10−8 T (d) 1. 41 × 10−8 T
6. Which of the following have zero average value in a plane electromagnetic wave?
(a) Electric energy (b) Magnetic energy
(c) Electric field (d) Magnetic field
7. An electromagnetic radiation has an energy 14.4 keV. To which region of electromagnetic spectrum does it belong?
(a) Infra-red region (b) Visible region
(c) X-ray region (d) γ − ray region
8. The condition under which a microwave oven heats up a food item containing water molecules most efficiently in
(a) the frequency of the microwave must match the resonant frequency of the water molecules.
(b) the frequency of the microwave has no relation with the natural frequency of water molecules.
(c) microwave are heatwaves, so always produce heating.
(d)infrared waves produce heating in a microwave oven.
- When an electromagnetic wave encounters a dielectric medium, the transmitted wave has
(a) same frequency but different amplitude.
(b) same amplitude but different frequency.
(c) same frequency and amplitude.
(d) different frequency and amplitude.
10. An electromagnetic wave going through the vacuum is described by E = E0 sin(kx − ωt). Which is the following is/are independent of the wavelength?
(a) k (b) k/ω
(c) k ω (d) ω
11. Statement I : Light can travel in vacuum but sound cannot do so. Statement II : Light is an electromagnetic wave and sound is a mechanical wave.
(a) If both Statement – I and Statement – II are true, and Statement – II is the correct explanation of Statement – I
(b) If both Statement – I and Statement – II are true but Statement – II is not the correct explanation of Statement I.
(c) If Statement – I is true but Statement – II is false.
(d) If Statement – I is false but Statement – II is ture.
12. In electromagnetic wave the phase difference between electric and magnetic field vectors E and B
(a) π/4 (b) π
(c) π/2 (d) 0
13. The oscillating electric and magnetic field vectors of an electromagnetic waves far away from source are oriented along
(a) Mutually perpendicular direction and differ in phase by 900
(b) Mutually perpendicular and in same phase.
(c) In same direction on and in same phase.
(d) In same direction on and differ in phase by 90o.
14. Consider an oscillator which has a charged particle oscillating about its mean position with a frequency of 300 MHz. The wavelength of electromagnetic waves produced by this oscillator is
(a) 100 m (b) 10 m (c) 1 m (d) 1000 m
15. Maxwell’s equation describes the fundamental laws of
(a) Electricity only (b) Magnetism only
(c) Mechanics only (d) Both (a) and (b)
1. c 2.a 3. d 4. d 5. a 6. c 7. c 8. a 9. a 10. b 11.a 12. d 13. b 14. c 15. d
MCQs on Optics
- A plane mirror approaches a stationary person with acceleration 10 ms–2. The acceleration of his image as seen by the person, will be
(a) 10 m/s2 (b) 20 m/s2
(c) 5 m/s2 (d) 4m/s2
2. A car is moving on a straight road at a speed of 50 km/h and a truck is ahead of the car and has a large plane mirror fixed vertically on the back of the truck. The truck is running at a speed of 70 km/h. For a stationary observer standing between car and truck, what is the speed of the image of the car in the mirror?
(a) 70 km/h (b) 20 km/h (c) 40 km/h (d) 90 km/h
3. An object is placed 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of a radius of curvature of 10 cm. The position of the image from the pole of the mirror is:
(a) 5.67 cm (b) 6.67 cm (c) 3.67 cm (d) 7.67 cm
4. A thin rod of length f/3 lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. One end of its magnified, real image touches an end of the rod. The length of the image is
(a) f (b) 2f (c) ½ f (d) f/4
5. A concave mirror gives an image three times as large as the object placed at a distance of 20 cm from it. For the image to be real, the focal length should be:
(a) 10 cm (b) 15 cm (c) 20 cm (d) 30 cm
6. A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is equal to the refractive index of the lens. Then its focal length will:
(a) become zero. (b) remain unchanged.
(c) become small, but non-zero. (d) become infinite.
7. A man with hypermetropia cannot see objects closer than a distance of 40 cm from the eye. The power of the lens required so that he can see objects at 25 cm from the eye is
(a) +4.5D (b) +4.0D (c) 1.5D (d) +3.0D
8. To increase the magnifying power of a telescope:
(a) the focal length of the eyepiece should be increased.
(b) the focal length of the objective should be increased.
(c) the wavelength of light should be increased.
(d) the aperture of the eyepiece should be increased.
- Two-point light sources are 24 cm apart. Where should a convex lens of focal length 9 cm be put in between them from one source so that the images of both the sources are formed at the same place?
(a) 8 cm (b) 12 cm (c) 9 cm (d) 6 cm
10. If the space between two convex lenses of glass in the combination shown in the figure below is filled with water, then:
 (a) the focal length of the system will decrease.
(a) the focal length of the system will decrease.
(b) the focal length of the system will increase.
(c) the power of the system will increase.
(d) the power of system will become infinite.
11. Two convex lenses of focal lengths 10 cm and 30 cm are kept at a separation of 20 cm. Then the correct statement is:
(a) the effective focal length is 15 cm.
(b) chromatic aberration is minimized.
(c) combination behaves like a convergent lens.
(d) All of these.
12. For a plane convex lens (µ = 1.5) has radius of curvature 10 cm. It is silvered on its plane surface. Find focal length after silvering.
(a) 10 cm (b) 22 cm (c) 35 cm (d) 25 cm
13. An air bubble in a glass slab with refractive index 1.5 (near-normal incidence) is 5 cm deep when viewed from one surface and 3 cm deep when viewed from the opposite face. The thickness (in cm) of the slab is :
(a) 8 (b) 6 (c) 12 (d) 18
14. A concave lens of focal length 25 cm produces an image
1/10 th the size of the object. The distance of the object from the lens is
(a) 225 cm (b) 230 cm (c) 130 cm (d) 145 cm
15. A square of side 3 cm is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. The centre of the square is at the axis of the mirror and the plane is normal to the axis. The area enclosed by the image of the square is
(a) 6 cm2 (b) 16 cm2 (c) 4cm2 (d) 5 cm2
1. b 2.a 3. b 4. c 5. b 6. d 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. b11.d 12. a 13. c 14. a 15. c
MCQs on Atoms & Nuclei
- In Bohr model the hydrogen atom, the lowest orbit corresponds to
(a) Infinite energy (b) zero energy
(c) The minimum energy (d) The maximum energy
2. The volume occupied by an atom is greater than the volume of the nucleus by a factor of about
(a) 10 (b) 105 (c) 1010 (d) 1015
3. The ratio of total acceleration of the electron in singly ionized helium atom and hydrogen atom (both in ground state) is
(a) 1 (b) 8 (c) 4 (d) 16
4. Like angular momentum, which another physical quantity is quantized in Bohr’s model of a hydrogen atom?
(a) Kinetic energy (b) Magnetic moment
(c) Potential energy (d) Mechanical energy
5. The binding energy per nucleon in deuterium and helium nuclei are 1. 1 MeV 7. 0 MeV, respectively. When and two deuterium nuclei fuse to form a helium nucleus, the energy released in the fusion is
(a) 47.12 MeV (b) 34.4 MeV
(c) 11.8 MeV (d) 23.6 MeV
6. Which of the following cannot be emitted in radioactive decay of the substance?
(a) Helium-nucleus (b) Proton
(c) Neutrinos (d) Electron
7. Ratio of longest wave lengths corresponding to Lyman and Blamer series in hydrogen spectrum is :
(a) 3/23 (b) 7/29 (c) 5/27 (d) 9/31
8. A freshly prepared radioactive source of half-life 2 hrs. emits radiations of intensity which is 64 times the permissible safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with the source is
(a) 6 hrs. (b) 12 hrs. (c) 24 hrs. (d) 128 hrs.
- Half-life of a radioactive substance is 20 minutes. The time between 20% and 80% decay will be
(a) 20 minutes (b) 40 minutes (c) 30 minutes (d) 25 minutes
10. A s the electron in Bohr is orbit t of hydrogen atom Passes from state n=2 to n=1, the K.E. and Potential energy changes as
(a) Two-fold , two-fold (b) four-fold , two-fold
(c) four-fold , four-fold (d) two-fold , four-fold
11. A heavy nucleus at lest breaks into two fragments which fly off with velocities in the ratio 8:1 The ratio of radial of the fragments is
(a) 1:2 (b) 4:1 (c)1:4 (d) 2:1
12. Whenever a hydrogen atom emits a photon in the Balmer series:
(a) It may emit another photon in the Balmer series.
(b) It must emit another photon in the Lyman series.
(c) It may emit another photon in the Paschen series.
(d) It need not emit any more photon.
13. The activity of a radioactive substance decays from 8000 becquerel to 4000 becquerel in 5 days. The activity of the substance after the next 10 days will be:
(a) 500 becquerel (b) 1500 becquerel
(c) 2000 becquerel (d) 1000 becquerel
14. Fusion reaction takes place at high temperature because
(a) atoms get ionised at high temperature.
(b) kinetic energy is high enough to overcome the Coulomb repulsion between nuclei.
(c) molecules break up at high temperature.
(d) nuclei break up at high temperature.
15. Hydrogen atom in ground state is excited by a monochromatic radiation of λ=975Å. The number of spectral lines in the resulting spectrum emitted will be:
(a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 6 (d) 10
1. c 2. d 3. b 4. a 5. d 6. d 7. c 8. b 9. b 10. c 11.a 12.b 13. d 14. b 15. c
MCQs on Electronic Devices
- Choose the only false statement from the following:
(a) The resistivity of a semiconductor increases with an increase in temperature.
(b) Substances with an energy gap of the order of 10eV are insulators.
(c) In conductors, the valence and conduction bands may overlap.
(d) The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increases in temperature.
2. A semiconductor is known to have an electron concentration of 8 × 1013 and hole concentration of 5 × 102 cm-3. The semiconductor is
(a) p -type (b) n-type (c) intrinsic (d) insulator
3. The net charges on p-type semiconductor and n-type semiconductor is, respectively:
(a) Positive, negative (b) Negative, positive
(c) Positive, positive (d) Zero, zero
4. The forbidden gap in the energy bands of germanium at room temperature is about
(a) 1.1 eV (b) 0.1 eV (c) 0.67 eV (d) 6.7 eV
5. If in a reverse-biased p − n junction, an increase in carrier concentration takes place due to the creation of new hole-electron pairs by the light of wavelength less than or equal to 620 nm, then the bandgap is:
(a) 1 eV (b) 2 eV (c) 20 eV (d) 0.2 eV
6. In which of the following condition, diffusion current in p – n junction is more than drift current ?
(a) Forward biasing (b) Reverse biasing
(c) No biasing (d) All of these
7. When forward bias is applied to a P-N junction, then what happens to the potential barrier , and the width of charge depleted region x
(a) VB increases, x decreases
(b) VB decreases, x increases
(c) VB increases, x increases
(d) VB decreases, x decreases
8. In a p–n junction photocell, the value of the photo electromotive force produced by monochromatic light is proportional to:
(a) The intensity of the light falling on the cell.
(b) The frequency of the light falling on the cell.
(c) The voltage applied at the p–n junction.
(d) The barrier voltage at the p–n junction.
- Which of the following-junction is used unbiased?
(a) Photo diode (b) LED (c) Zener diode (d) Solar cell
10. When a transistor is used as a switch it is in:
(a) Active state. (b) Cut off state.
(c) Saturation state. (d) Both cut off state and saturation state are possible.
11. A combination of logic gates is shown in the circuit. If A is at 0 V and B is at 5 V, then the potential of R is:

(a) 0 V (b) 5 V (c) 10 V (d) 15 V
12. A gate has the following truth table
P 1 1 0 0
Q 1 0 1 0
R 1 0 0 0
The gate is
(a) NOR (b) OR (c) NAND (d) AND
13. The circuit is equivalent to:
![]()
(a) NOR (b) OR (c) NAND (d) AND
14. An NPN transistor conducts when
(a) Both collector and emitter are positive with respect to the base.
(b) the collector is positive and the emitter is negative with respect to the base.
(c) the collector is positive and the emitter is at the same potential as the base.
(d) both collector and emitter are negative with respect to the base.
15. In a common emitter transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector is 3V. The resistance of collector is 3k Ω . If current gain is 100 and the base resistance is 2k Ω , the voltage and power gain of the amplifier is
(a) 200 and 1000 (b) 15 and 200
(c) 150 and 15000 (d) 20 and 2000
1. a 2. b 3. d 4. c 5. b 6. a 7. d 8. d 9. d 10. 11.a 12.d 13. a 14. b 15. c

